LoadingCache
简介
loadingCache也叫本地缓存,简单来说就是将数据放到在内存里,需要的时候直接从内存取,减少数据库/redis网络io,提高查询效率,之前在快手很多地方都运用这个技术,不过只局限于使用,原理还不懂。
快速使用
引入依赖,这里我们使用谷歌的guava工具类
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>27.1-jre</version>
</dependency>创建cache实例并且调用
package org.example;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheBuilder;
import com.google.common.cache.CacheLoader;
import com.google.common.cache.LoadingCache;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class LoadingCacheTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 LoadingCache,支持批量加载
LoadingCache<String, User> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.refreshAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build(new CacheLoader<String, User>() {
@Override
public User load(String key) throws Exception {
// 单个加载逻辑
System.out.println("单个加载: " + key);
return fetchUserFromSource(key);
}
@Override
public Map<String, User> loadAll(Iterable<? extends String> keys) throws Exception {
// 批量加载逻辑
System.out.println("批量加载 " + keys);
return fetchUsersFromSource((Set<? extends String>) keys);
}
});
try {
// 模拟批量获取数据
Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>();
keys.add("user1");
keys.add("user2");
keys.add("user3");
Map<String, User> users = cache.getAll(keys); // 批量获取
users.forEach((key, user) -> System.out.println(key + ": " + user));
log.info("第一次获取数据: {}", users);
Map<String, User> users2 = cache.getAll(keys);
users2.forEach((key, user) -> System.out.println(key + ": " + user));
log.info("第二次获取数据: {}", users2);
User user = cache.get("user1");
log.info("第三次获取数据: {}", user);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.out.println("系统异常");
}
}
// 模拟从数据源加载单个 User 对象
private static User fetchUserFromSource(String userId) {
return new User(userId, "User-" + userId, 20 + userId.hashCode() % 30);
}
// 模拟从数据源批量加载 User 对象
private static Map<String, User> fetchUsersFromSource(Set<? extends String> userIds) {
// 模拟从数据库或其他数据源批量加载用户信息
Map<String, User> users = new HashMap<>();
users.put("user1", new User("user1", "John", 30));
users.put("user2", new User("user2", "Jane", 28));
users.put("user3", new User("user3", "Alice", 25));
return users;
}
}根据输出可以看到,第一次调用缓存获取数据会先加载,等第二次调用缓存的时候,就能直接获取到数据了。
批量加载 [user1, user2, user3]
user1: User{id='user1', name='John', age=30}
user2: User{id='user2', name='Jane', age=28}
user3: User{id='user3', name='Alice', age=25}
10:00:20.259 [main] INFO org.example.LoadingCacheTest - 第一次获取数据: {user1=User{id='user1', name='John', age=30}, user2=User{id='user2', name='Jane', age=28}, user3=User{id='user3', name='Alice', age=25}}
user1: User{id='user1', name='John', age=30}
user2: User{id='user2', name='Jane', age=28}
user3: User{id='user3', name='Alice', age=25}
10:00:20.263 [main] INFO org.example.LoadingCacheTest - 第二次获取数据: {user1=User{id='user1', name='John', age=30}, user2=User{id='user2', name='Jane', age=28}, user3=User{id='user3', name='Alice', age=25}}
10:00:20.264 [main] INFO org.example.LoadingCacheTest - 第三次获取数据: User{id='user1', name='John', age=30}参数介绍
maximumSize
缓存最大容量,当缓存的数据量超过这个值,会按照算法淘汰旧的数据,默认值-1。
public CacheBuilder<K, V> maximumSize(long maximumSize) {
Preconditions.checkState(this.maximumSize == -1L, "maximum size was already set to %s", this.maximumSize);
Preconditions.checkState(this.maximumWeight == -1L, "maximum weight was already set to %s", this.maximumWeight);
Preconditions.checkState(this.weigher == null, "maximum size can not be combined with weigher");
Preconditions.checkArgument(maximumSize >= 0L, "maximum size must not be negative");
this.maximumSize = maximumSize;
return this;
}expireAfterWrite
缓存项写入过期时间, 多久没更新就失效,默认值-1。
public CacheBuilder<K, V> expireAfterWrite(long duration, TimeUnit unit) {
Preconditions.checkState(this.expireAfterWriteNanos == -1L, "expireAfterWrite was already set to %s ns", this.expireAfterWriteNanos);
Preconditions.checkArgument(duration >= 0L, "duration cannot be negative: %s %s", duration, unit);
this.expireAfterWriteNanos = unit.toNanos(duration);
return this;
}expireAfterAccess
缓存项的访问过期时间,多久没访问(读/写)就失效,默认值-1。
public CacheBuilder<K, V> expireAfterAccess(long duration, TimeUnit unit) {
Preconditions.checkState(this.expireAfterAccessNanos == -1L, "expireAfterAccess was already set to %s ns", this.expireAfterAccessNanos);
Preconditions.checkArgument(duration >= 0L, "duration cannot be negative: %s %s", duration, unit);
this.expireAfterAccessNanos = unit.toNanos(duration);
return this;
}refreshAfterAccess
缓存数据重新加载的时间,默认值-1,保证只有一个线程refresh缓存,缺点是其他缓存返回旧值,get才会触发refresh。
public CacheBuilder<K, V> refreshAfterWrite(long duration, TimeUnit unit) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(unit);
Preconditions.checkState(this.refreshNanos == -1L, "refresh was already set to %s ns", this.refreshNanos);
Preconditions.checkArgument(duration > 0L, "duration must be positive: %s %s", duration, unit);
this.refreshNanos = unit.toNanos(duration);
return this;
}核心功能
初始化
build返回的是LocalLoadingCahe实例。
public <K1 extends K, V1 extends V> LoadingCache<K1, V1> build(CacheLoader<? super K1, V1> loader) {
this.checkWeightWithWeigher();
return new LocalCache.LocalLoadingCache(this, loader);
}再往下看构造函数,将cachebuilder和loader封装为LocalCache
LocalLoadingCache(CacheBuilder<? super K, ? super V> builder, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
super(new LocalCache(builder, (CacheLoader)Preconditions.checkNotNull(loader)), null);
}这里代码有点多,主要就是构造LocalCache对象,设置最大数量,过期时间等参数,同时声明segment数组,每个元素是类似hash表,目的是为了减少锁的竞争,具体的过程可以看下面代码。
LocalCache(CacheBuilder<? super K, ? super V> builder, @Nullable CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
this.concurrencyLevel = Math.min(builder.getConcurrencyLevel(), 65536);
this.keyStrength = builder.getKeyStrength();
this.valueStrength = builder.getValueStrength();
this.keyEquivalence = builder.getKeyEquivalence();
this.valueEquivalence = builder.getValueEquivalence();
this.maxWeight = builder.getMaximumWeight();
this.weigher = builder.getWeigher();
this.expireAfterAccessNanos = builder.getExpireAfterAccessNanos();
this.expireAfterWriteNanos = builder.getExpireAfterWriteNanos();
this.refreshNanos = builder.getRefreshNanos();
this.removalListener = builder.getRemovalListener();
this.removalNotificationQueue = (Queue<RemovalNotification<K, V>>)(this.removalListener == NullListener.INSTANCE ? discardingQueue() : new ConcurrentLinkedQueue());
this.ticker = builder.getTicker(this.recordsTime());
this.entryFactory = LocalCache.EntryFactory.getFactory(this.keyStrength, this.usesAccessEntries(), this.usesWriteEntries());
this.globalStatsCounter = (AbstractCache.StatsCounter)builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get();
this.defaultLoader = loader;
int initialCapacity = Math.min(builder.getInitialCapacity(), 1073741824);
if (this.evictsBySize() && !this.customWeigher()) {
initialCapacity = (int)Math.min((long)initialCapacity, this.maxWeight);
}
int segmentShift = 0;
int segmentCount;
for(segmentCount = 1; segmentCount < this.concurrencyLevel && (!this.evictsBySize() || (long)(segmentCount * 20) <= this.maxWeight); segmentCount <<= 1) {
++segmentShift;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - segmentShift;
this.segmentMask = segmentCount - 1;
this.segments = this.newSegmentArray(segmentCount);
int segmentCapacity = initialCapacity / segmentCount;
if (segmentCapacity * segmentCount < initialCapacity) {
++segmentCapacity;
}
int segmentSize;
for(segmentSize = 1; segmentSize < segmentCapacity; segmentSize <<= 1) {
}
if (this.evictsBySize()) {
long maxSegmentWeight = this.maxWeight / (long)segmentCount + 1L;
long remainder = this.maxWeight % (long)segmentCount;
for(int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) {
if ((long)i == remainder) {
--maxSegmentWeight;
}
this.segments[i] = this.createSegment(segmentSize, maxSegmentWeight, (AbstractCache.StatsCounter)builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get());
}
} else {
for(int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) {
this.segments[i] = this.createSegment(segmentSize, -1L, (AbstractCache.StatsCounter)builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get());
}
}
}最后将localCache对象传递给父构造函数
private LocalManualCache(LocalCache<K, V> localCache) {
this.localCache = localCache;
}get
调用localCache对象的getOrLoad方法
public V get(K key) throws ExecutionException {
return this.localCache.getOrLoad(key);
}本质是通过哈希运算,找到对应的段下表,调用段的get方法
V get(K key, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
int hash = this.hash(Preconditions.checkNotNull(key));
return (V)this.segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash, loader);
}
Segment<K, V> segmentFor(int hash) {
// 找到对应下表
return this.segments[hash >>> this.segmentShift & this.segmentMask];
}最终的get方法如下: 根据key获取没过期的元素,如果获取到值,判断是否要refresh,如果没获取到值,判断其他线程是否在loading,如果是就等待,如果其他线程没有在加载,则自己加载。
我们从代码可以看出,loadingCache是先判断缓存有没有过期,再判断是否需要刷新。
V get(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(key);
Preconditions.checkNotNull(loader);
try {
if (this.count != 0) {
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = this.getEntry(key, hash);
if (e != null) {
long now = this.map.ticker.read();
// 获取没过期的值
V value = (V)this.getLiveValue(e, now);
// 存在
if (value != null) {
this.recordRead(e, now);
this.statsCounter.recordHits(1);
// 判断是否需要refresh
Object var17 = this.scheduleRefresh(e, key, hash, value, now, loader);
return (V)var17;
}
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
// 判断其他线程是否在加载该值
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {
Object var9 = this.waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference);
return (V)var9;
}
}
}
// 自己去加载值
Object var15 = this.lockedGetOrLoad(key, hash, loader);
return (V)var15;
} catch (ExecutionException ee) {
Throwable cause = ee.getCause();
if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw new ExecutionError((Error)cause);
} else if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(cause);
} else {
throw ee;
}
} finally {
this.postReadCleanup();
}
}load方法如下:
1、获得锁。
2、获得key对应的valueReference。
3、判断是否该缓存值正在loading,如果loading,则不再进行load操作(通过设置createNewEntry为false),后续会等待获取新值。
4、如果不是在loading,判断是否已经有新值了(被其他请求load完了),如果是则返回新值。
5、准备loading,设置为loadingValueReference。loadingValueReference 会使其他请求在步骤3的时候会发现正在loding。
6、释放锁。
7、如果真的需要load,则进行load操作。
加锁是以段为单位的,所以其他线程在访问同个段时会阻塞。
V lockedGetOrLoad(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = null;
LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference = null;
boolean createNewEntry = true;
this.lock();
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e;
try {
long now = this.map.ticker.read();
this.preWriteCleanup(now);
int newCount = this.count - 1;
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
int index = hash & table.length() - 1;
// 根据key获取当前段的table下标(段本质是一个哈希表,由数组和链表组成)
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = (ReferenceEntry)table.get(index);
// 从链表里面找到当前key所在的元素
for(e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
K entryKey = (K)e.getKey();
if (e.getHash() == hash && entryKey != null && this.map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) {
valueReference = e.getValueReference();
// 判断是否正在被其他线程加载
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {
createNewEntry = false;
} else {
V value = valueReference.get();
if (value == null) {
// 将缓存加入通知队列,代表被移除
this.enqueueNotification(entryKey, hash, value, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.COLLECTED);
} else {
if (!this.map.isExpired(e, now)) {
this.recordLockedRead(e, now);
this.statsCounter.recordHits(1);
Object var16 = value;
return (V)var16;
}
this.enqueueNotification(entryKey, hash, value, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.EXPIRED);
}
this.writeQueue.remove(e);
this.accessQueue.remove(e);
this.count = newCount;
}
break;
}
}
// 创建新节点
if (createNewEntry) {
loadingValueReference = new LoadingValueReference<K, V>();
if (e == null) {
e = this.newEntry(key, hash, first);
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
// 覆盖原有节点
table.set(index, e);
} else {
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
}
}
} finally {
this.unlock();
this.postWriteCleanup();
}
if (createNewEntry) {
Object var9;
try {
synchronized(e) {
// 加载新的值
var9 = this.loadSync(key, hash, loadingValueReference, loader);
}
} finally {
this.statsCounter.recordMisses(1);
}
return (V)var9;
} else {
return (V)this.waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference);
}
}refresh代码如下: 判断是否需要refresh并且不处于loading状态,如果是直接refresh,返回新值,其他情况返回旧值。
可以看出,如果有其他线程在在load,就直接返回旧的值。
V scheduleRefresh(ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry, K key, int hash, V oldValue, long now, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
if (this.map.refreshes() && now - entry.getWriteTime() > this.map.refreshNanos && !entry.getValueReference().isLoading()) {
V newValue = (V)this.refresh(key, hash, loader, true);
if (newValue != null) {
return newValue;
}
}
return oldValue;
}getAll
码如下: 1、 遍历keys,获取不存在的key集合。 2、调用loadAll方法。
ImmutableMap<K, V> getAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys) throws ExecutionException {
int hits = 0;
int misses = 0;
Map<K, V> result = Maps.newLinkedHashMap();
Set<K> keysToLoad = Sets.newLinkedHashSet();
for (K key : keys) {
// 获取对应key的值
V value = get(key);
if (!result.containsKey(key)) {
result.put(key, value);
// 如果值不存在,添加到keysToLoad集合
if (value == null) {
misses++;
keysToLoad.add(key);
} else {
hits++;
}
}
}
try {
if (!keysToLoad.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 批量加载不存在的key
Map<K, V> newEntries = loadAll(keysToLoad, defaultLoader);
for (K key : keysToLoad) {
V value = newEntries.get(key);
if (value == null) {
throw new InvalidCacheLoadException("loadAll failed to return a value for " + key);
}
result.put(key, value);
}
} catch (UnsupportedLoadingOperationException e) {
// loadAll not implemented, fallback to load
// 出现异常则循环调用get方法
for (K key : keysToLoad) {
misses--; // get will count this miss
result.put(key, get(key, defaultLoader));
}
}
}
return ImmutableMap.copyOf(result);
} finally {
globalStatsCounter.recordHits(hits);
globalStatsCounter.recordMisses(misses);
}
}这里的get方法不是之前的get,之前的get要调我们重写load方法,这里不用,找不到返回null, 下面再进行批量调用。
@Nullable
V get(Object key, int hash) {
try {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile
long now = map.ticker.read();
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getLiveEntry(key, hash, now);
if (e == null) {
return null;
}
V value = e.getValueReference().get();
if (value != null) {
recordRead(e, now);
return scheduleRefresh(e, e.getKey(), hash, value, now, map.defaultLoader);
}
tryDrainReferenceQueues();
}
return null;
} finally {
postReadCleanup();
}
}loadAll方法如下
@Nullable
Map<K, V> loadAll(Set<? extends K> keys, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader)
throws ExecutionException {
checkNotNull(loader);
checkNotNull(keys);
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.createStarted();
Map<K, V> result;
boolean success = false;
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // safe since all keys extend K
// 调用真正的loadAll函数
Map<K, V> map = (Map<K, V>) loader.loadAll(keys);
result = map;
success = true;
} catch (UnsupportedLoadingOperationException e) {
success = true;
throw e;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new ExecutionException(e);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(e);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExecutionException(e);
} catch (Error e) {
throw new ExecutionError(e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
globalStatsCounter.recordLoadException(stopwatch.elapsed(NANOSECONDS));
}
}
if (result == null) {
globalStatsCounter.recordLoadException(stopwatch.elapsed(NANOSECONDS));
throw new InvalidCacheLoadException(loader + " returned null map from loadAll");
}
stopwatch.stop();
// TODO(fry): batch by segment
boolean nullsPresent = false;
for (Entry<K, V> entry : result.entrySet()) {
K key = entry.getKey();
V value = entry.getValue();
if (key == null || value == null) {
// delay failure until non-null entries are stored
nullsPresent = true;
} else {
put(key, value);
}
}
if (nullsPresent) {
globalStatsCounter.recordLoadException(stopwatch.elapsed(NANOSECONDS));
throw new InvalidCacheLoadException(loader + " returned null keys or values from loadAll");
}
// TODO(fry): record count of loaded entries
globalStatsCounter.recordLoadSuccess(stopwatch.elapsed(NANOSECONDS));
return result;
}如果没重写loadAll方法,会抛出异常,外面会for循环调用get方法加载数据。
public Map<K, V> loadAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys) throws Exception {
// This will be caught by getAll(), causing it to fall back to multiple calls to
// LoadingCache.get
// 没有重写,则抛出异常
throw new UnsupportedLoadingOperationException();
}缓存回收方式
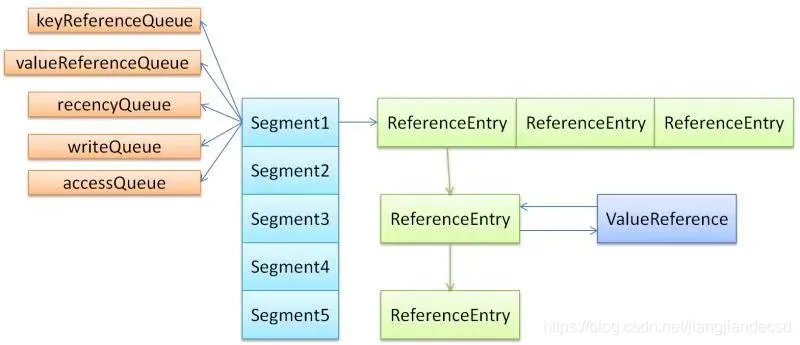
队列
GuavaCache会维护两个队列,一个writeQueue、一个accessQueue,用这两个队列来实现最近读和最近写的清除操作。
Segment(
LocalCache<K, V> map,
int initialCapacity,
long maxSegmentWeight,
StatsCounter statsCounter) {
this.map = map;
this.maxSegmentWeight = maxSegmentWeight;
this.statsCounter = checkNotNull(statsCounter);
initTable(newEntryArray(initialCapacity));
keyReferenceQueue = map.usesKeyReferences() ? new ReferenceQueue<K>() : null;
valueReferenceQueue = map.usesValueReferences() ? new ReferenceQueue<V>() : null;
recencyQueue =
map.usesAccessQueue()
? new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>()
: LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue();
// 写队列
writeQueue =
map.usesWriteQueue()
? new WriteQueue<K, V>()
: LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue();
// 访问队列
accessQueue =
map.usesAccessQueue()
? new AccessQueue<K, V>()
: LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue();
}读写操作都会对队列进行修改
@GuardedBy("this")
void recordWrite(ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry, int weight, long now) {
// we are already under lock, so drain the recency queue immediately
drainRecencyQueue();
totalWeight += weight;
if (map.recordsAccess()) {
entry.setAccessTime(now);
}
if (map.recordsWrite()) {
entry.setWriteTime(now);
}
accessQueue.add(entry);
writeQueue.add(entry);
}这里的add本质上调用了offer,offer进行了重写,将当前元素移动到队列末尾。
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}基于容量的回收
如果要规定缓存项的数目不超过固定值,只需使用CacheBuilder.maximumSize(long)。缓存将尝试回收最近没有使用或总体上很少使用的缓存项,采用LRU算法回收缓存。 调用地方: put、get等方法。
void evictEntries(ReferenceEntry<K, V> newest) {
// 是否开启最大条目限制
if (!map.evictsBySize()) {
return;
}
// 将最近操作的元素移动到assess队列后面
drainRecencyQueue();
// If the newest entry by itself is too heavy for the segment, don't bother evicting
// anything else, just that
//如果新插入的条目非常大(例如,它的权重超过了 maxSegmentWeight),
//则只需要移除这个新条目,而不需要驱逐其他条目。
if (newest.getValueReference().getWeight() > maxSegmentWeight) {
if (!removeEntry(newest, newest.getHash(), RemovalCause.SIZE)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
// 移除其他条目
while (totalWeight > maxSegmentWeight) {
// 获取要移除的元素
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getNextEvictable();
if (!removeEntry(e, e.getHash(), RemovalCause.SIZE)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainRecencyQueue() {
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e;
while ((e = recencyQueue.poll()) != null) {
// An entry may be in the recency queue despite it being removed from
// the map . This can occur when the entry was concurrently read while a
// writer is removing it from the segment or after a clear has removed
// all of the segment's entries.
if (accessQueue.contains(e)) {
accessQueue.add(e);
}
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
ReferenceEntry<K, V> getNextEvictable() {
for (ReferenceEntry<K, V> e : accessQueue) {
int weight = e.getValueReference().getWeight();
if (weight > 0) {
return e;
}
}
throw new AssertionError();
}定时回收
expireAfterAccess(long, TimeUnit):缓存项在给定时间内没有被读/写访问,则回收。请注意这种缓存的回收顺序和基于大小回收一样。 expireAfterWrite(long, TimeUnit):缓存项在给定时间内没有被写访问(创建或覆盖),则回收。如果认为缓存数据总是在固定时候后变得陈旧不可用,这种回收方式是可取的。
注:使用CacheBuilder构建的缓存不会"自动"执行清理和回收工作,也不会在某个缓存项过期后马上清理,也没有诸如此类的清理机制。相反,它会在写操作时顺带做少量的维护工作,或者偶尔在读操作时做(如果写操作实在太少) get方法、containsKey、getAll都能触发。
@GuardedBy("this")
void expireEntries(long now) {
// 将最近操作的元素添加到access队列
drainRecencyQueue();
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e;
// 移除过期元素
while ((e = writeQueue.peek()) != null && map.isExpired(e, now)) {
if (!removeEntry(e, e.getHash(), RemovalCause.EXPIRED)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
while ((e = accessQueue.peek()) != null && map.isExpired(e, now)) {
if (!removeEntry(e, e.getHash(), RemovalCause.EXPIRED)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
}基于引用的回收
CacheBuilder.weakKeys():使用弱引用存储键。当键没有其它(强或软)引用时,缓存项可以被垃圾回收。
CacheBuilder.weakValues():使用弱引用存储值。当值没有其它(强或软)引用时,缓存项可以被垃圾回收。
CacheBuilder.softValues():使用软引用存储值。软引用只有在响应内存需要时,才按照全局最近最少使用的顺序回收。
写操作会触发。
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainReferenceQueues() {
if (map.usesKeyReferences()) {
drainKeyReferenceQueue();
}
if (map.usesValueReferences()) {
drainValueReferenceQueue();
}
}显示清除
个别清除:Cache.invalidate(key)。
批量清除:Cache.invalidateAll(keys)。
清除所有缓存项:Cache.invalidateAll()。
 hongshen
hongshen